|
 |
| Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
Adult, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
Adult, striped form, San Clemente Island
© Bob Haase |
Adult, San Clemente Island
© Bob Haase |
Adult, San Clemente Island
© Bob Haase |
 |
 |
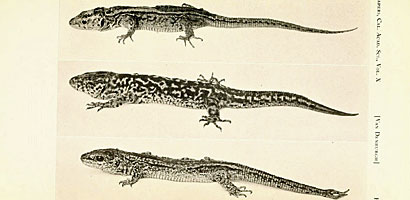
Top and bottom: Xantusia riversiana from San Nicolas Island
Middle: Xantusia riversiana from Santa Barbara Island
From "The reptiles of western North America v.I (1922) by Biodiversity Heritage Library contributed by Smithsonian Libraries.
|
Island Night Lizards have small granular scales on soft skin. |
| |
|
|
| Habitat |
 |
 |
 |
| Santa Barbara Island |
Santa Barbara Island |
Santa Barbara Island and Sutil Islet,
early Summer |
 |
 |
 |
Santa Barbara Island,
early Summer |
Grassy plateau, top of
Santa Barbara Island |
View looking down at Elephant Seal Beach, Santa Barbara Island |
 |
 |
 |
Rocky cliff-edge and Sutil Islet, early Summer, Santa Barbara Island
|
Dormant Giant Coreopsis, Santa Barbara Island, early summer |
 |
 |
 |
| Santa Barbara Island, early Summer |
Santa Barbara Island landing area |
Santa Barbara Island, early Summer |
 |
 |
 |
| Santa Barbara Island with Spring greenery and blooming Giant Coreopsis © Tim Burkhardt |
|
|
|
| Description |
| |
| Size |
2.5 - 4.2 inches long from snout to vent (6.3 - 10.6 cm). (Stebbins 2003)
The largest of the Xantusiids, growing from about 5 - 8 inches long including the tail.
|
| Appearance |
A medium-sized lizard with granular scales, soft skin that appears loose around the neck and shoulders, large plates on the head, lidless eyes with vertical pupils, a gular fold, and a fold of skin low on each side of the body.
Two rows of supraoculars and 16 lengthwise rows of squarish scales at the midbelly. |
| Color and Pattern |
Color and pattern are variable - Brown, olive-brown, grayish, rusty, or yellowish-brown with a reticulated pattern of dark brown or black spots or blotches, sometimes with full or broken light stripes edged with black along the sides of the back.
Striped lizards occur on San Clemente Island, but rarely on Santa Barbara Island.
The underside is slate bluish, cream or pale yellow.
The undersides of the feet are sometimes yellowish.
|
| Life History and Behavior |
Activity |
Once considered nocturnal, but apparently diurnal but sedentary, secretive, and rarely seen.
Spends most of its time under cover, but occasionally seen exposed on the surface in daylight.
The mild climate of the islands this lizard inhabits allows it to remain active throughout the year.
Grows and matures slowly, living to at least 12 years old |
| Defense |
The tail can break off easily, but it will grow back.
The detached tail wriggles on the ground which can distract a predator from the body of the lizard allowing it time to escape.
More information about tail loss and regeneration. |
| Diet and Feeding |
| Eats small invertebrates including insects, spiders, scorpions, and marine isopods along with plant material (which can make up to one-third of its diet.) |
| Reproduction |
Reproductive potential is low.
Adults do not reach sexual maturity
until their 3rd or 4th year and only about half of all females reproduce each year.
Breeds in March and April.
Viviporous, bearing 2-9 live young mostly in September.
|
| Habitat |
Found in almost any island habitat that provides it protection and shade - maritime desert scrub, grassland, chaparral, oak savanna, cactus, dry stream beds, cliffs, rocky beaches, sparsely-vegetated areas. Takes shelter in cracks in rocks or in the ground, and under surface objects such as rocks, fallen vegetation and beach driftwood.
Santa Barbara Island is a flat tree-less plateau with grasses, small shrubs, introduced ice plant, prickly-pear cactus and Giant Coreopsis. There are a few small rocky canyons along the edge with dense vegetation.
|
| Geographical Range |
Endemic to California.
Found only on islands off the southern California coast - Santa Barbara Island, Sutil Islet, and San Clemente Island.
|
| Notes on Taxonomy |
Two subspecies of Xantusia riversiana have been recognized:
Xantusia riversiana reticulata - San Clemente Night Lizard
Xantusia riversiana riversiana - San Nicolas Night Lizard
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Not all authorities recognize the two subspecies that are shown on this web site. Below are some examples.
"Although not mentioned by Noonan et al. (2013, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 69: 109–122), their results support the taxonomic distinction between populations of X. riversiana on San Nicolas Island (X. r. riversiana) and those on San Clemente and Santa Barbara Islands (X. r. reticulata). "
(SSAR Herpetological Circular No. 43, 2017.)
"Overall, the San Clemente and Santa Barbara populations are more similar to each other than either is to San Nicolas. Lizards from San Nicolas reach a larger size and have larger litters than on San Clemente and Santa Barbara. Subtle differences in color and color pattern are also evident among the populations, with San Nicolas having the greatest variation. The island populations do not differ substantially in allozymes, but the DNA data (Nonan et al. 2013) weakly support the two described subspecies: X. r. riversiana on San Nicolas and X. riversiana reticulata on San Clemente and Santa Barbara (Smith 1946, Savage 1963, Wermuth 1965, Fellers and Drost 1991, Adams et al. 2018). In this book I do not use subspecies names due to the larger number of geographically isolated populations of xantusiids with scale features that differ statistically but have overlapping ranges of variation."
(Robert L. Bezy. Night Lizards. 2019)
Hansen and Shedd 2025 - recognizes two subspecies
SSAR List 2025 - recognizes two subspecies (see note below)
iNaturalist 1/25 - recognizes two subspecies
Wikipedia 1/25 - recognizes two subspecies
The Reptile Database 1/25 - recognizes two subspecies
Stebbins & McGinnis 2012 and 2018 - recognizes no subspecies
SSAR List 2017 - recognizes two subspecies
Stebbins 2003 - recognizes no subspecies
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"The standard English name for this clade has been changed (by adding “Northern”), following Bezy (2019, Night Lizards, Eco Herpetological Publishing), to eliminate redundancy with the English name of the clade Xantusiidae."
(Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025 SSAR Scientific and Standard English Names List)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"The taxonomic distinction between populations of X. riversiana on San Nicolas Island (X. r. riversiana) and those on San Clemente and Santa Barbara Islands (X. r. reticulata) has been supported by analyses of both DNA sequences (Noonan et al., 2013, Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 69: 109–122) and morphology (Adams et al., 2018, Copeia 106: 550–562; Grismer et al., 2022, Vertebrate Zoology 7: 1–27)."
(Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025 SSAR Scientific and Standard English Names List)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Alternate and Previous Names (Synonyms)
Xantusia riversiana - Island Night Lizard (Stebbins 1985, 2003)
Klauberina riversiana - Island NIght Lizard (Stebbins 1966)
Xantusia riversiana - Island Night Lizard (Smith 1946, Stebbins 1954)
Xantusia riversiana - Island Night Lizard (Rivers's Lizard) (Grinnell and Camp 1917)
|
| Conservation Issues (Conservation Status) |
Protected since 1967. This lizard's restricted habitat has been threatened by the grazing of introduced livestock and game, (most of which have now been removed) and by introduced predators such as feral cats and possibly rats. It is also preyed upon heavily by native birds and mammals. In 1990 the USFWS categorized the status of lizards on San Clemente Island as stable.
A 1991 study by Fellers and Drost determined that the population on Santa Barbara Island is not threatened.
The U.S. Navy administers San Clemente and San Nicolas Islands, and has petitioned to have lizards from those islands removed from the Endangered Species List. Santa Barbara Island and Sutil Islet are protected as National Park property.
On 4/1/14 the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service removed Xantusia riversiana, the island night lizard, from the Federal List of Endangered and Threatened Wildlife. More Information |
|
|
Taxonomy |
| Family |
Xantusiidae |
Night Lizards |
Baird, 1858 |
| Genus |
Xantusia |
Northern Night Lizards |
Baird, 1859 “1858” |
| Species |
riversiana |
Island Night Lizard |
Cope, 1883 |
Subspecies
|
reticulata |
San Clemente Night Lizard |
Smith, 1946 |
|
Original Description |
Xantusia riversiana - Cope, 1883 - Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia, Vol. 35, p. 29
Xantusia riversiana reticulata - Smith, 1946 - Journ. Washington Acad. Sci., Vol. 36, p. 392
from Original Description Citations for the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Meaning of the Scientific Name |
Xantusia - honors Xantus, John
riversiana - honors Rivers, James, J.
reticulata - Latin = net-like - probably refers to the pattern.
from Scientific and Common Names of the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America - Explained © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Related or Similar California Lizards |
X. gracilis - Sandstone Night Lizard
X. henshawi - Granite Night Lizard
X. r. riversiana - San Nicolas Night Lizard
X. sierrae - Sierra Night Lizard
X. vigilis - Yucca Night Lizard
X wigginsi - Wiggins' Night Lizard
|
|
More Information and References |
California Department of Fish and Wildlife
US Fish & Wildlife Service
IUCN Red List
Robert L. Bezy. Night Lizards: Field Memoirs and a Summary of the Xantusiidae. ECO Herpetological Publishing & Distribution. 2019.
Hansen, Robert W. and Shedd, Jackson D. California Amphibians and Reptiles. (Princeton Field Guides.) Princeton University Press, 2025.
Stebbins, Robert C., and McGinnis, Samuel M. Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Revised Edition (California Natural History Guides) University of California Press, 2012.
Stebbins, Robert C. California Amphibians and Reptiles. The University of California Press, 1972.
Flaxington, William C. Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Field Observations, Distribution, and Natural History. Fieldnotes Press, Anaheim, California, 2021.
Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025. Scientific and Standard English Names of Amphibians and Reptiles of North America North of Mexico, with Comments Regarding Confidence in Our Understanding. Ninth Edition. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. [SSAR] 87pp.
Samuel M. McGinnis and Robert C. Stebbins. Peterson Field Guide to Western Reptiles & Amphibians. 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2018.
Stebbins, Robert C. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians. 3rd Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2003.
Behler, John L., and F. Wayne King. The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Reptiles and Amphibians. Alfred A. Knopf, 1992.
Robert Powell, Roger Conant, and Joseph T. Collins. Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America. Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2016.
Powell, Robert., Joseph T. Collins, and Errol D. Hooper Jr. A Key to Amphibians and Reptiles of the Continental United States and Canada. The University Press of Kansas, 1998.
Thelander, C. G., ed. Life on the Edge: A Guide to California's Endangered Natural Resources Volume I: Wildlife.
Biosystems Books, Santa Cruz, California. 1994.
Schoenherr, Allan A. Natural History of the Islands of California. The University of California Press. 2003.
Fellers, G.M. and Drost, C.A. 1991. Xantusia riversiana. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 516: 1-4.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). 1990. Endangered and threatened species recovery program: report to Congress.
Bartlett, R. D. & Patricia P. Bartlett. Guide and Reference to the Turtles and Lizards of Western North America (North of Mexico) and Hawaii. University Press of Florida, 2009.
Jones, Lawrence, Rob Lovich, editors. Lizards of the American Southwest: A Photographic Field Guide. Rio Nuevo Publishers, 2009.
Smith, Hobart M. Handbook of Lizards, Lizards of the United States and of Canada. Cornell University Press, 1946.
Taylor, Emily. California Lizards and How to Find Them. Heyday, Berkeley, California. 2025.
Joseph Grinnell and Charles Lewis Camp. A Distributional List of the Amphibians and Reptiles of California. University of California Publications in Zoology Vol. 17, No. 10, pp. 127-208. July 11, 1917.
|
|
|
The following conservation status listings for this animal are taken from the July 2025 State of California Special Animals List and the July 2025 Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list (unless indicated otherwise below.) Both lists are produced by multiple agencies every year, and sometimes more than once per year, so the conservation status listing information found below might not be from the most recent lists, but they don't change a great deal from year to year.. To make sure you are seeing the most recent listings, go to this California Department of Fish and Wildlife web page where you can search for and download both lists:
https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Data/CNDDB/Plants-and-Animals.
A detailed explanation of the meaning of the status listing symbols can be found at the beginning of the two lists. For quick reference, I have included them on my Special Status Information page.
If no status is listed here, the animal is not included on either list. This most likely indicates that there are no serious conservation concerns for the animal. To find out more about an animal's status you can also go to the NatureServe and IUCN websites to check their rankings.
Check the current California Department of Fish and Wildlife sport fishing regulations to find out if this animal can be legally pursued and handled or collected with possession of a current fishing license. You can also look at the summary of the sport fishing regulations as they apply only to reptiles and amphibians that has been made for this website.
The July 2023 Special Animals List and Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list designations apply to the full species, Xantusia riversiana - Island Night Lizard.
|
| Organization |
Status Listing |
Notes |
| NatureServe Global Ranking |
G3 |
Vulnerable—At moderate risk of extinction due to a restricted range, relatively few populations (often 80 or fewer), recent and widespread declines, or other factors. |
| NatureServe State Ranking |
S3 |
Vulnerable in the state due to a restricted range, relatively few populations (often 80 or fewer), recent and widespread declines, or other factors making it vulnerable to extirpation from the state. |
| U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) |
Recovered & Delisted |
FT - Listed as Threatened 9/12/1977
FPD - Federally Proposed (Delisting) 2/4/2013
Recovered - Removed from ESA list 5/1/2014
|
| California Endangered Species Act (CESA) |
None |
|
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife |
None |
|
| Bureau of Land Management |
None |
|
| USDA Forest Service |
None |
|
| IUCN |
LC |
Least Concern |
|
|