|
This species has been introduced into California. It is not a native species.
|
 |
| Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult female, St. Lucie County, Florida |
Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
Adult male, St. Lucie County, Florida |
The skinks shown above are all from the Florida population. Pictures of skinks from California can be found on iNatualist. |
| |
| Description |
| |
| Size |
3.5. - 5.25 inches long, snout-to-vent (8.9 - 13.3 cm).
Tail can be up to 1.5 times the body length.
(Powell, Conant, & Collins, 2016)
|
| Appearance |
A medium-sized stocky lizard with a cylindrical body, a pointed snout, small ear openings, moveable eyelids, round pupils, no femoral pores, and strong, well-developed legs with relatively long toes. Cycloid scales are underlaid by bony plates. Dorsal scales are almost entirely keeled, though the appearance is smooth. Ventral scales are similar to dorsals.
Coloration is variable, depending on the gender and the age.
Females and juveniles
The basic color is dark brown to black, with whitish spots along the front part of the sides and five cream to yellowish longitudinal stripes extending from the head to the tail along the back and sides - three stripes on the back, and one stripe on each side. The dorsal stripes fade sometimes, becoming indistinct on adults. The stripes gradually change to blue on the tail, with the tip of the tail completely blue. Re-generated tails are brown. The underside is white.
Adult Males
Light to dark brown above, without longitudinal stripes. The Side of the head and neck are black with a light blue stripe on the upper lip and light blue spots on the side of the neck and the upper flanks. The throat and breast and rear side of the head are black with white spots, the venter is white to bluish gray. A yellow to orange stripe is usually visible from the lips to the forelimbs, gradually fading on the sides. The tail is brownish.
|
| Life History and Behaviors |
Diurnal.
Primarily terrestrial, sometimes climbing rocks and trees. Around human habitation can be found on fences and walls.
Often seen basking in sunlight. |
| Diet |
Omnivorous - eats mostly invertebrates, flowers, small lizards, and fruit.
|
| Reproduction and Young |
The species is oviparous. The female lays 6-10 eggs in summer. The young hatch after 61-62 days. Females may lay two clutches per season. (Siyabona Africa)
Females may guard the eggs.
|
| Habitat |
In its native habitat, found in rocky and grassland habitats, on trees, and on human structures.
In California, found in suburban neighborhoods in the San Gabriel Valley.
|
| Range |
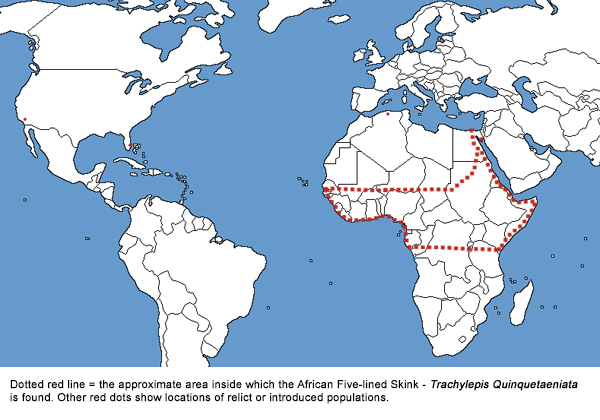
Worldwide Distribution
Native to a large part of sub-Saharan Africa, with a relict population found recently in northern Algeria.. "Trachylepis quinquetaeniata has a wide native distribution in eastern, central, and western Africa, from Kenya through the arid sub-Saharan belt west to Senegal (Spawls et al. 2002), and has at least one non-indigenous population in Egypt (Kraus 2009)." (Krysko et al. 2010).
(Some sources show T. quinquetaeniata also present along the east coast of southern Africa, south to the cape of South Africa, but that area is not included in the description of countries where the skink is found that is included on The Reptile Database, so I have left this area off my distribution map until I can verify that the skinks in that area are T. quinquetaeniata and not a different species.)
Documented by Krysko et al. in 2010 as established in Port St. Lucie, St. Lucie County, Florida. Skinks in Florida were introduced via the pet trade from a pet dealer's former warehouse directly across the street from the researcher's study site.
An apparent population of T. quinquetaeniata has also been found in south Miami.
Distribution In California
Originally discovered in Glendora in the San Gabriel Valley in eastern Lost Angeles County. As of January 2022 there are several records on iNatualist dating from 2016-2020 that are shown on the map as Baldwin Park, Azusa, Glendora, and City of Industry and elsewhere, but since the actual locations of the records have been obscured, the locations shown on the map are not accurate. I have been informed that all of the skinks were found in the same area of Glendora and also that eradication efforts there have apparently been successful and that no skinks have been reported from the area since 2020.
Origins of California Population
An established population of this species was first recorded in Glendora in eastern Los Angeles County in 2018 after being reported on iNaturalist. (Pauly and Gavit, 2019) The species is found in the reptile trade. The skinks in the original population in Glendora are thought to be derived from skinks kept by a reptile dealer living in the neighborhood, who imported some of them from Egypt in September 2014. Other exotic reptiles have been observed roaming free in the neighborhood, too. Residents report that there was a rapid population increase of African Five-lined Skinks in the summer and fall of 2018. (Pauly and Gavit, 2019).
|
 |
| Taxonomic Notes |
Two subspecies are recognized of this species:
Trachylepis quinquetaeniata quinquetaeniata (Lichtenstein, 1823)
Trachylepis quinquetaeniata riggenbachi (Sternfeld, 1910)
|
| Conservation Issues (Conservation Status) |
It is not evident how competition from this introduced species impacts native species, but the spread of this or any non-native species should be discouraged.
It's likely that this species will compete with native lizard species for resources, most likely Sceloporus occidentalis and Elgaria multicarinata.
"One neighborhood resident reported a decline in S. occidentalis with the increasing occurrence of T. quinquetaeniata in his backyard." (Pauly and Gavit, 2019)
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
| Family |
Scincidae |
Skinks |
Gray, 1825 |
| Genus |
Trachylepis |
Afro-Malagasy mabuyas |
Fitzinger, 1843 |
| Species |
quinquetaeniata |
African Five-lined Skink |
(Lichtenstein, 1823) |
| Subspecies |
Not known
|
|
|
|
Original Description |
Lichtenstein, 1823
|
|
Meaning of the Scientific Name
|
Trachylepis means rough-scaled
Greek - trachys = rough or stony
Greek - lepis = scale or peel - which refers to the keeled scales
quinquetaeniata - refers to the five stripes
Latin - quinque = five
Latin - taenia = band
|
|
Alternate Names
|
Mabuya quinquetaeniata
Five-lined Mabuya
Rainbow Mabuya
Rainbow Skink
Rainbow Rock Skink
|
|
Related or Similar California Herps
|
Coronado Skink - Plestiodon skiltonianus interparietalis
Skilton's Skink - Plestiodon skiltonianus skiltonianus
|
|
More Information and References
|
Gregory B. Pauly and Patrick D. Gavid. Geographical Distribution Note. Herpetological Review 50(1), 2019
Robert Powell, Roger Conant, and Joseph T. Collins. Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America. Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2016.
The Reptile Database
iNatualist
Wikipedia
Naturserve Explorer
Krysko, K. L., S. A. Johnson, K. E. Giddens, K. H. Gielow, T. S. Lowke, W. M. Moore, E. Suarez, C. D. Thomas, A. S. Shoeslon, J. P. Burgess, C. A. Smith, and B. A. Garner. 2010. The African five-lined skink, Trachylepis quinquetaeniata (Lichtenstein 1823): a new established species in Florida. IRCF Reptiles & Amphibians 17(3):183-184
Siyabona Africa
|
|
|
The following conservation status listings for this animal are taken from the July 2025 State of California Special Animals List and the July 2025 Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list (unless indicated otherwise below.) Both lists are produced by multiple agencies every year, and sometimes more than once per year, so the conservation status listing information found below might not be from the most recent lists, but they don't change a great deal from year to year.. To make sure you are seeing the most recent listings, go to this California Department of Fish and Wildlife web page where you can search for and download both lists:
https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Data/CNDDB/Plants-and-Animals.
A detailed explanation of the meaning of the status listing symbols can be found at the beginning of the two lists. For quick reference, I have included them on my Special Status Information page.
If no status is listed here, the animal is not included on either list. This most likely indicates that there are no serious conservation concerns for the animal. To find out more about an animal's status you can also go to the NatureServe and IUCN websites to check their rankings.
Check the current California Department of Fish and Wildlife sport fishing regulations to find out if this animal can be legally pursued and handled or collected with possession of a current fishing license. You can also look at the summary of the sport fishing regulations as they apply only to reptiles and amphibians that has been made for this website.
|
| Organization |
Status Listing |
Notes |
| NatureServe Global Ranking |
|
|
| NatureServe State Ranking |
|
|
| U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) |
None |
|
| California Endangered Species Act (CESA) |
None |
|
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife |
None |
|
| Bureau of Land Management |
None |
|
| USDA Forest Service |
None |
|
| IUCN |
|
|
|
|
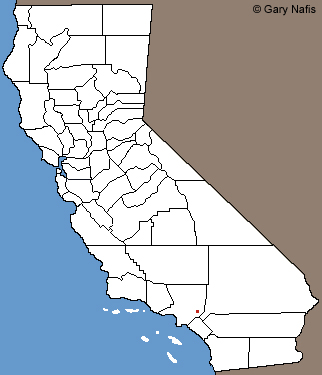 Red: Areas where this non-native species has been reported
Red: Areas where this non-native species has been reported 








