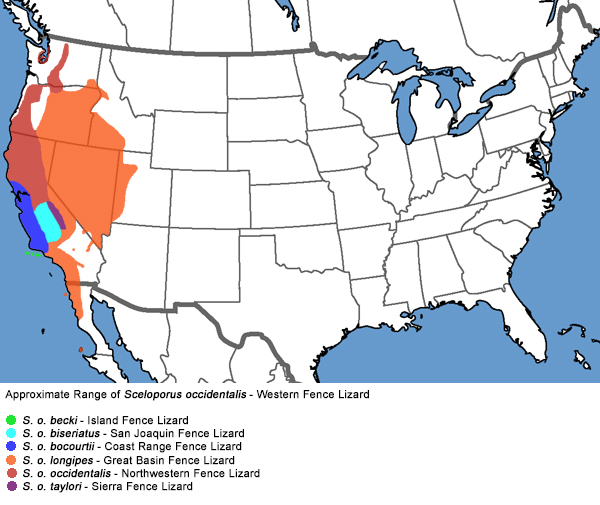
Western Fence Lizard - Sceloporus occidentalis
Coast Range Fence Lizard - Sceloporus occidentalis bocourtii
Boulenger, 1885Description • Taxonomy • Species Description • Scientific Name • Alt. Names • Similar Herps • References • Conservation Status
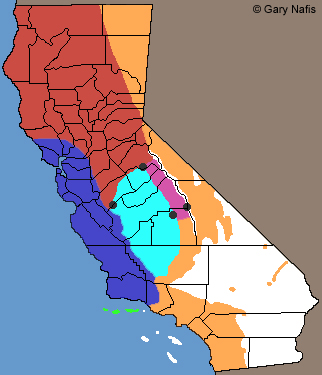 Dark Blue: Range of this subspecies in California
Dark Blue: Range of this subspecies in CaliforniaSceloporus occidentalis bocourtii - Coast Range Fence Lizard
Range of other subspecies in California:
Bright Blue: Sceloporus occidentalis biseriatus -
San Joaquin Fence Lizard
Orange: Sceloporus occidentalis longipes -
Great Basin Fence Lizard
Red: Sceloporus occidentalis occidentalis -
Northwestern Fence Lizard
Purple: Sceloporus occidentalis taylori -
Sierra Fence Lizard
Dark Gray: Hybrid Zones
Bright Green: Sceloporus becki -
Island Fence Lizard
Click on the map for a topographical view
Map with California County Names
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult female, San Benito County |
Adult female, Alameda County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult male, Santa Clara County © Yuval Helfman | Adult, Solano County |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult male, Napa County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult, Contra Costa County | Adult female, San Mateo County | Adult female, Contra Costa County | Adult male, Contra Costa County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult male, Contra Costa County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult male, Contra Costa County | Adult male, Monterey County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult female, San Mateo County | Adult female, Contra Costa County | Adult, Monterey County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Most adult male Western Fence Lizards have pale coloring on the throat and venter around the patches of blue, but some are black like this male found in southern Napa County during the breeding season. His blue coloring is also very intense. © Ryne Starling |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult, Marin County © Lou Silva | Adult, Contra Costa County | Adult male, Santa Clara County © Yuval Helfman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult, San Luis Obispo County © Ryan Sikola | Adult male, Alameda County, playing dead after being released. © Yuval Helfman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult female, San Luis Obispo County | Adult with a nice view of the Golden Gate Bridge from a stone lookout at the crest of the East Bay Hills, Contra Costa County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult, San Francisco County © Luke Talltree |
Adult, Alameda County © David Rodriguez Sometimes fence lizards are very dark before they have warmed up in the sun, like this one. They can look like they're completely black at a distance. This can cause problems for some people trying to identify a lizard that doesn't look like a typical fence lizard they see in pictures. |
Adult female, San Luis Obispo County © Joel A. Germond |
Very dark adult male, San Luis Obispo County © Joel A. Germond | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two adults in San Luis Obispo County, showing how they can be variable in color. © Joel A. Germond | Two adult females sharing a basking spot in early Fall in San Luis Obispo County © Joel A. Germond | Adult male, Santa Clara County (notice that the throat is not blue.) © Yuval Helfman After release from capture, this lizard remained motionless in the position seen here for about a minute before turning over and running away. |
Adult, Marin county, showing salt excreted from its nares (nostrils). © 2001 Guntram Deichsel |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two different species of lizards, an adult Skilton's Skink and a Coast Range Fence Lizard, were observed basking together frequently in a backyard garden in Marin County in April. This might represent a mate-guarding behavior by a male skink that confused the fence lizard with a female skink, or maybe they're just sharing a good basking spot, unconcerned about any threat from the other lizard. | Adult, San Luis Obispo County, with several ticks in its ear opening. © Ryan Sikola |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult male with ticks on the side of his head and in his ear. In California, western black-legged ticks (deer ticks) are the primary carriers of Lyme disease. Very tiny nymphal deer ticks are more likely to carry the disease than adults. A protein in the blood of Western Fence Lizards kills the bacterium in these nymphal ticks when they attach themselves to a lizard and ingest the lizard's blood. This could explain why Lyme disease is less common in California than it is in some areas such as the Northeastern states, where it is epidemic. More Information |
Western Fence Lizards have overlapping keeled scales with spines on them over much of their body. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unusually-Colored Coast Range Fence Lizards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This unusually-colored lizard was photographed in February in Contra Costa County. © Alice Castellanos Occasionally I receive pictures of similarly-colored spiny lizards, but I have not learned what causes the unusual color, whether it is a naturally-occurring aberrant coloration, or if it is artificially added somehow by chemicals or by spores and pollen. You can see more pictures of orange or gold spiny lizards on this page. |
Tiny albino hatchling, missing part of its tail, from Alameda County. (Photographed with an old Polaroid camera in the late 1970s that would not focus on the tiny lizard.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adult female with bright orange coloring, Marin County, © Rosey Rosenke | Albino hatchling found in late September, Santa Clara County © Amanda Law | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypomelanistic juvenile, Marin County © Emile Bado |
Hypomelanistic juvenile, Marin County © Adam Gitmed |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Juveniles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hatchling in early August, Santa Clara County © Yuval Helfman |
Hatchling in early August, Contra Costa County |
Hatchling in early August, Contra Costa County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Juvenile, Contra Costa County | Juvenile, Contra Costa County | Juvenile, Contra Costa County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Male Combat and Other Breeding Season Behavior | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two colorful adult males fighting during the May breeding season, San Luis Obispo County. © Joel A. Germond | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On a sunny afternoon in May in Contra Costa County, the adult male on top chased the female on the bottom, keeping on top of her and not letting her get away. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feeding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This San Luis Obispo County Coast Range Fence Lizard crept up to an adult Antlion, lunged to catch it, then swallowed it whole. © Joel A. Germond | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sean Kelly © shot this series of a California Striped Racer eating a male Great Basin Fence lizard in San Diego County. | Juvenile fence lizards are preyed upon by many other animals, including the black widow spider. © Rory Doolin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| An adult Coast Range Fence Lizard eating a juvenile of the same species in San Luis Obispo County. © Joel A. Germond | A California Striped Racer swallows a male Northwestern Fence Lizard in El Dorado County © Jim Bennett |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coast Gartersnake eating a Coast Range Fence Lizard in San Luis Obispo County © Joel Germond |
Juvenile Pacific Gopher Snake eating a Western Fence Lizard © Daniel Harris | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| California Striped Racers eat mosly lizards. This one is swallowing a Western Fence Lizard while holding the front third of its body straight up off the ground. This racer usually hunts with its head in this elevated position. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Habitat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Habitat, Contra Costa County | Sandy wash with rocky edge habitat, San Benito County |
Lizard in habitat, Alameda County | Habitat, Napa County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Habitat, Monterey County |
Habitat, San Luis Obispo County | Habitat, Contra Costa County | Coastal dunes habitat, Monterey County | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Habitat, East Bay Hills, Contra Costa County |
Coastal scrub habitat, Marin County | Habitat, Contra Costa County |
Habitat, Contra Costa County |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Habitat, Contra Costa County | Habitat, San Mateo County | Habitat, Sonoma County | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short Videos of Coast Range Fence Lizards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A few fence lizards in Contra Costa County. | A male fence lizard on a tree in Alameda County. | Several juvenile fence lizards come out to bask in the sun on a cool and windy morning in early March. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two Coast Range Fence Lizards observed during the breeding season in early May in San Benito County. The first lizard, a female, has moved from her perch on a rock to a nearby rock in order to get away from the photographer. She begins a territorial push-up display when a male comes up the side of the rock and begins to pursue her. She arches her back and hops away in order to reject him. She may have already mated and is bearing eggs, or maybe he is not her type. He finally stops and does a push-up display, possibly to continue trying to entice her, or possibly to warn the photographer that this is his territory. | Two male fence lizards on the edge of a paved road in San Luis Obispo County size each other up for 20 seconds until one of them makes a move on the other starting a slight skirmish, that ends up as more of a test than a fight. © Joel A. Germond |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short Videos of Other Subspecies of Western Fence Lizard | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A male Northwestern Fence Lizard defecates off the side of a Butte County fence, wipes himself off, then does a territorial push-up display. | I'm not going out of my way trying to film this behavior - I can only take what I get - so here we see another Northwestern Fence Lizard doing his business for the camera. It's like they're trying to tell me something. | A male Northwestern Fence Lizard fights with a female in Placer County © Rod | San Joaquin Fence Lizards on trees along a river in early spring. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sierra Fence lizards run around a rocky area in the woods 8,000 ft. high in the Sierra Nevada mountains. | A Sierra Fence Lizard, or intergrade, runs around rocks in the forest up at 5,600 ft. in Tuolumne County. | A female fence lizard runs across a wall in Riverside County and encounters a male who pursues her. She rejects him and he runs to an open spot on top of the wall and does a push-up display. | A male fence lizard in Inyo County defensively showing his throat color and doing push-ups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Large, dark phase Great Basin Fence Lizards bask and eat ants off rocks in Inyo County. |
These two videos show a Placer County Northwestern Fence Lizard appearing to taunt a garter snake (a Mountain Gartersnake is my guess, because it lacks red.) The lizard keeps moving down towards the snake but when the snake moves towards the lizard, apparently trying to catch it for dinner, the lizard runs up the wall away from the snake. © Rod | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following conservation status listings for this animal are taken from the July 2025 State of California Special Animals List and the July 2025 Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list (unless indicated otherwise below.) Both lists are produced by multiple agencies every year, and sometimes more than once per year, so the conservation status listing information found below might not be from the most recent lists, but they don't change a great deal from year to year.. To make sure you are seeing the most recent listings, go to this California Department of Fish and Wildlife web page where you can search for and download both lists: https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Data/CNDDB/Plants-and-Animals. A detailed explanation of the meaning of the status listing symbols can be found at the beginning of the two lists. For quick reference, I have included them on my Special Status Information page. If no status is listed here, the animal is not included on either list. This most likely indicates that there are no serious conservation concerns for the animal. To find out more about an animal's status you can also go to the NatureServe and IUCN websites to check their rankings. Check the current California Department of Fish and Wildlife sport fishing regulations to find out if this animal can be legally pursued and handled or collected with possession of a current fishing license. You can also look at the summary of the sport fishing regulations as they apply only to reptiles and amphibians that has been made for this website. This animal is not included on the Special Animals List, which indicates that there are no significant conservation concerns for it in California. |
||
| Organization | Status Listing | Notes |
| NatureServe Global Ranking | ||
| NatureServe State Ranking | ||
| U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) | None | |
| California Endangered Species Act (CESA) | None | |
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife | None | |
| Bureau of Land Management | None | |
| USDA Forest Service | None | |
| IUCN | ||
|
|
||
Return to the Top
© 2000 -